Implementing SPF, DKIM, DMARC & BIMI
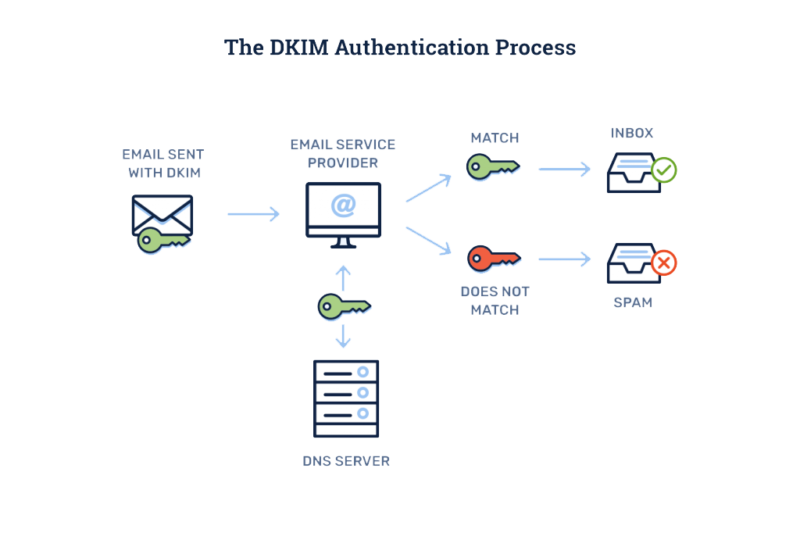
The very best approach to securing your domain’s email is to layer DKIM with SPF and validate it with DMARC.
BIMI is a layer on top of DMARC which adds your logo to the avatar section of an email.
We like to empower our clients, existing and prospective especially whent we believe some people can do it for themselves. As such we’ve created a 3 step guide for you to follow.
Alternatively, we can set all of this up for you. If you have access to the domain registrar login and the admin panel for the email server this can be done in as little as 1 hour per domain, if we have to transfer domains or reconfigure your name servers, this may require time for the internet to see the changes, it’s much like you moving house and updating your address, except it takes between 2 hours and 48 hours vs days for the automatic updates to propagate. This means the project can easily become 2-3hrs (or more) however once you provide the information to us, we can tell you very quickly how long it will take so you can decide if you’d like us to continue.
We charge $150 for the first hour to configure SPF, DKIM and DMARC and then $100 per hour after that. 95% of our clients require less than 2 hours, however this may be over 2 zoom sessions using screensharing where I take control of your browser, then, for security reasons, you don’t need to share your passwords with me.
We offer DMARC monitoring for $5 per domain per month through glockapps.com, for this we will report back any issues as they occur up to 5,000 emails per month.
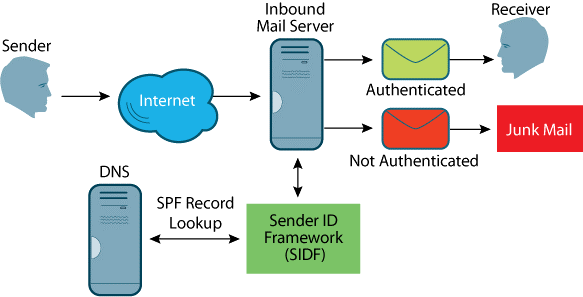
SPF. Sender Policy Framework
SPF is an email authentication protocol that allows the owner of a domain to specify which mail servers they use to send mail from that domain.
During an SPF check, email providers verify the SPF record by looking up the domain name listed in the “envelope from” address in the DNS. If the IP address sending email on behalf of the “envelope from” domain isn’t listed in that SPF record, the message fails SPF authentication..
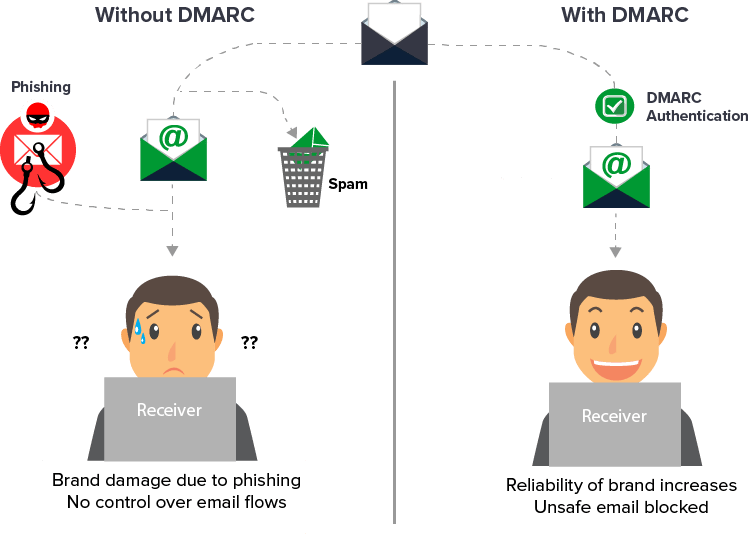
DMARC. Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance
With DMARC, a domain owner can specify its own authentication procedure (known as a DMARC policy). Using it, they instruct an incoming server on what to do if an email fails to pass the DMARC test. Finally, the policy can also provide reports with the details of each check to improve processes and provide immediate warning if anyone spoofs the account.
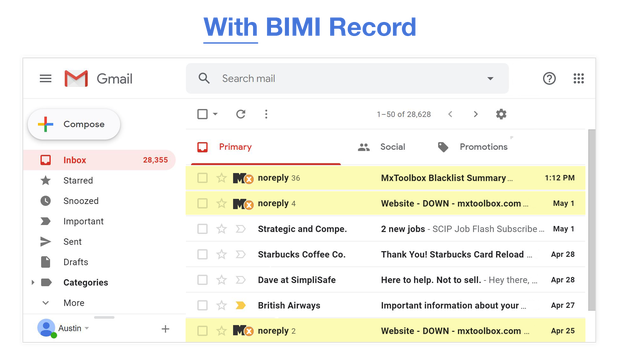
BIMI. Brand Indicators for Message Identification
BIMI is a way to verify information about your brand. Like DMARC, DKIM, and SPF—three methods for verifying sender information—BIMI is a text record that lives on your servers. In fact, it works right alongside SPF, DMARC, and DKIM to signal to email clients that you are you.
BIMI is different in that it also allows you to display your company logo in supported inboxes, putting your brand front-and-center for subscribers.